What is protective grounding, surge proof grounding, and ESD grounding? What's the difference?
There are three types of grounding:
Functional grounding: grounding of an electrical system or equipment required for operation.
Protective grounding: To prevent the metal shell of electrical equipment from being damaged by insulation and endangering the safety of human, animal and equipment, and to set up the corresponding protection system, the metal shell or other metal structure of electrical equipment with no electrical charge is grounded.
Repeated grounding: To enhance the grounding function and effect of the grounding protection system and improve its reliability, ground another ground at one or more places of the ground cable.
There are three types of functional grounding:
Working grounding: refers to the grounding of the electrical system to stabilize the normal working voltage. (e.g. grounding of neutral points of transformers and generators)
Shielded grounding: grounding the exposed conductive part of an electrical line or device to prevent the internal conductor or device from external electromagnetic interference. (e.g. cable metal sheath, threaded metal pipe and grounding of metal casing of electronic components)
Logical grounding: To ensure the stable operation of electronic equipment with its metal base plate or a common connection wire as a potential reference point of logic signal grounding.
There are three types of protective grounding:
Protective grounding: refers to grounding the exposed conductive part of the electrical equipment in the grounding protection system.
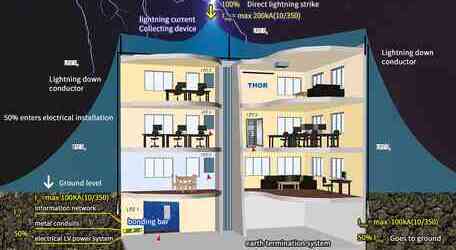
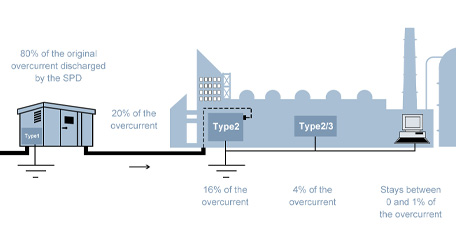
Lightning protection grounding: In order to prevent the lightning electrical system and equipment, as well as the elevated metal facilities and buildings, structures caused by the lightning protection device, lightning current can be discharged into the ground smoothly when the lightning protection device is grounded. (such as grounding of flash and arrester)
Antistatic grounding: To prevent the static electricity generated during the operation of the electrical system or equipment from harming people, animals, and property, and to smoothly import the harmful static electricity into the ground, ground the site where the static electricity is generated.
The above is the difference between protective grounding, surge proof grounding, and anti-static grounding.